 |
(7) |
Using the IUPAC naming system, how many of the C5H12 constitutional isomers will have a name ending in "pentane"?
|
 |
(8) |
The least stable conformation of 1,2-dichloroethane is
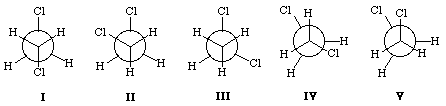
|
 |
(9) |
Which of the following C6H12 isomers would have the highest heat of combustion?
|
(Use the following information for questions 10-11.) Again, considering the polar reaction we used in class for an example of reaction mechanisms and the following reaction profile:
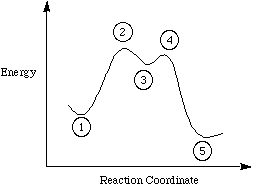
 |
(10) |
Which point(s) represent transition state(s)?
|
 |
(11) |
Which point(s) represent an intermediate?
|
|
